IPTV OTT Encoding & Streaming
Hardware Acceleration with NVIDIA NVENC/NVDEC GPU
Understanding NVIDIA GPU Hardware Acceleration
What is NVIDIA NVENC and NVDEC?
 NVIDIA GPUs contain one or more hardware-based decoder and encoder
units (separate from the CUDA cores) that provide fully-accelerated video decoding and
encoding for several popular codecs. With GPU decoding and encoding via NVENC and NVDEC
SDKs, IPVTL offloads heavy computational tasks from the CPU, freeing it for other
applications. This specialized hardware delivers significantly faster transcoding compared
to software-based encoding.
NVIDIA GPUs contain one or more hardware-based decoder and encoder
units (separate from the CUDA cores) that provide fully-accelerated video decoding and
encoding for several popular codecs. With GPU decoding and encoding via NVENC and NVDEC
SDKs, IPVTL offloads heavy computational tasks from the CPU, freeing it for other
applications. This specialized hardware delivers significantly faster transcoding compared
to software-based encoding.
Benefits of GPU-Accelerated Video Encoding
Hardware GPU encoding with NVENC provides multiple advantages for professional video streaming: dramatically reduced CPU utilization (enabling higher channel throughput), lower latency in transcoding pipelines, reduced power consumption compared to software encoding, and the ability to maintain real-time performance with multiple simultaneous encoding sessions. NVIDIA GPU acceleration is ideal for broadcast environments, OTT platforms, and high-volume transcoding operations.
GPU Support Matrix and Codec Compatibility
Before selecting NVIDIA video cards, visit the NVIDIA Video Encode and Decode GPU Support Matrix to ensure the card meets your codec requirements. Different GPU generations support different video codecs: GeForce RTX 40-series supports H.264, HEVC, and AV1, while older models may support only H.264 and HEVC. Professional Quadro and Tesla cards offer broader codec support and more encoding sessions.
NVIDIA GPU Setup and Configuration
Set up NVIDIA GPU Streaming on Windows
To set up NVIDIA GPU streaming on Windows, desktop operating systems like Windows 10 and
Windows 11 are recommended over server OS for optimal driver support. Make sure to install
the latest NVIDIA video driver from NVIDIA Official Drivers. After
driver installation, verify the installation by running nvidia-smi in Command
Prompt to display GPU information and driver version.
Set up NVIDIA GPU Streaming on Linux
To enable NVIDIA GPU streaming on Linux, recent Linux distributions such as Ubuntu are recommended, as they provide better support for the latest NVIDIA video drivers. For example, Ubuntu includes the ubuntu-drivers tool for easy NVIDIA driver installation. For detailed instructions, visit Ubuntu NVIDIA Drivers Installation. Always install the latest video driver, as GPU encoding may not function with outdated drivers.
Verifying GPU Installation with nvidia-smi
After driver installation on any OS, run nvidia-smi in a terminal to verify
the installation and display GPU hardware information:
# nvidia-smi
Wed Dec 11 09:52:10 2019
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| NVIDIA-SMI 536.23 Driver Version: 536.23 CUDA Version: 12.2 |
|-----------------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
| GPU Name TCC/WDDM | Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. ECC |
| Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap | Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. |
| | | MIG M. |
|=========================================+======================+======================|
| 0 Tesla K80 On | 00000000:00:1E.0 Off | N/A |
| 0% 43C P0 7W / 149W | 639MiB / 11441MiB | 1% Default |
| | | N/A |
+-----------------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Processes: |
| GPU GI CI PID Type Process name GPU Memory |
| ID ID Usage |
|=======================================================================================|
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
GPU Encoding Session Limitations
NVIDIA GeForce GTX/RTX series and Quadro models below K2000/M2000/P2000/T2000 have a
maximum of 8 or 12 encoding sessions per system. This is a hard limit enforced by the
NVIDIA driver. Other Quadro models, Tesla, and GRID cards do not have this limitation.
Professional applications requiring more than 12 simultaneous streams should consider Tesla
or enterprise-grade GPU options.
To bypass the GeForce encoding limit on consumer cards
(use at your own risk), follow the instructions at https://github.com/keylase/nvidia-patch
for a third-party driver patch.
NVIDIA Video Encoding Configuration
Set up NVIDIA Video Encoding
IPVTL supports H.264, HEVC, and AV1 encoding on NVIDIA GPUs. In channel configuration, select encodings with NVENC to enable GPU encoding. This offloads the primary computational burden from the system CPU to the dedicated NVIDIA encoding engine.
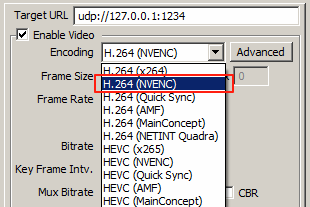
GPU Codec Support and RTX Card Capabilities
Different NVIDIA video cards have different video encoding capabilities. For example, GeForce RTX 4090, RTX 4080, and RTX 4060 support AV1 encoding, while GeForce RTX 3090, RTX 3060, and GTX 1660 do not. For comprehensive details on each GPU's encoding capabilities, visit NVIDIA Video Encode and Decode GPU Support Matrix. Refer to this matrix before purchasing GPU hardware to ensure it meets your specific codec requirements.
Multi-GPU Load Balancing
When multiple NVIDIA GPUs are installed in a single system, IPVTL can distribute encoding workload across all available GPUs. Configure separate channels to use different GPU devices for optimal load balancing and maximum throughput. This configuration is ideal for high-volume transcoding operations requiring multiple simultaneous encoding streams.
NVIDIA Video Decoding Configuration
Set up NVIDIA Video Decoding
If the channel source video is encoded in H.264, HEVC, or MPEG-2, you can enable NVDEC to perform full GPU transcoding. Select H.264 or HEVC with NVDEC/CUVID (matching your source video format) in advanced video settings > Misc. > GPU Decoding. This performs all video decoding, resizing, and encoding operations (including deinterlacing if required) on the GPU, avoiding unnecessary data transfers between system memory and video memory.
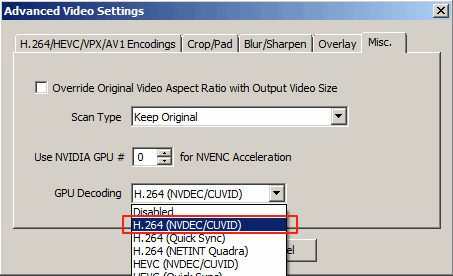
Full GPU Pipeline Transcoding
When both NVDEC decoding and NVENC encoding are enabled on the same GPU, IPVTL creates a complete GPU pipeline where video data never leaves GPU memory between decode and encode stages. This zero-copy architecture maximizes throughput and minimizes latency, making it ideal for real-time streaming applications. Full GPU transcoding is most efficient when processing large numbers of simultaneous streams.
GPU Device Selection and Multi-Card Routing
If you have multiple NVIDIA cards installed, specify which card to use in the settings above to balance the GPU load. For example, assign NVDEC operations to GPU 0 and NVENC operations to GPU 1 to distribute computational load. This configuration can significantly improve throughput in high-volume transcoding scenarios.
GPU Performance Monitoring and Optimization
Monitor NVIDIA GPU Load
The GPU-Z tool can monitor NVIDIA GPU load on Windows. Go to the Sensors tab > Video Engine Load reflects the current NVDEC/NVENC load. Note that this is different from "GPU Load", which reflects 3D-rendering load instead. If you have multiple video cards, select them in IPVTL advanced video options and monitor them separately to maintain proper load balancing. Alternatively, you can use the GPU load monitor available in Windows 10 Task Manager and later.

Linux GPU Monitoring Tools
On Linux, use nvidia-smi or nvtop for comprehensive GPU
monitoring. Both tools display real-time NVDEC/NVENC load, memory utilization, temperature,
and power consumption. Run nvidia-smi dmon for a continuous display of GPU
metrics, or watch -n 1 nvidia-smi to auto-refresh every second.
GPU Performance Tuning
Optimize NVIDIA GPU performance by monitoring encoding bitrate, frame rate consistency, latency metrics, and GPU utilization percentages. Adjust IPVTL encoding presets (Fast, Balanced, Quality) to find the optimal tradeoff between encoding speed and output quality for your application. Use GPU-Z or nvidia-smi to verify that encoding operations are consistently utilizing the GPU to avoid CPU bottlenecks.
NVIDIA GPU vs Alternative Hardware Acceleration
Comparison with Other Hardware Acceleration Options
NVIDIA GPUs offer powerful hardware acceleration for video transcoding with NVENC and NVDEC support. For alternative acceleration technologies, compare with Intel GPU encoding and NETINT VPU hardware encoder. Each technology has specific strengths: NVIDIA dominates encoding speed and codec breadth, Intel offers competitive performance with lower power consumption, and NETINT VPU specializes in high-density encoding.
GPU Selection for Streaming Applications
Choose the right GPU based on your requirements: GeForce RTX series for budget-conscious deployments up to 12 concurrent streams, Quadro RTX for professional workflows requiring more sessions, and Tesla for data center and unlimited encoding session applications. Consider total cost of ownership including power consumption, cooling requirements, and software licensing.
Integration with IPVTL Streaming Features
NVIDIA GPU acceleration integrates seamlessly with IPVTL's other features:
- HLS streaming with GPU-accelerated multi-bitrate encoding
- MPEG-DASH for adaptive bitrate with GPU transcoding
- RTMP protocol delivery with hardware-accelerated NVENC encoding
- SRT low-latency streaming with GPU optimization
- Professional video codecs optimized for NVIDIA hardware
- Adaptive bitrate streaming using GPU multi-encoding
- Video overlay and graphics with GPU-accelerated rendering
- Seamless streaming transitions with uninterrupted GPU encoding
GPU Acceleration Benchmarking
Before deployment, benchmark your NVIDIA GPU hardware against your specific workflow: test the number of simultaneous H.264, HEVC, and AV1 streams it can handle, measure CPU utilization with GPU encoding enabled vs disabled, and compare encoding latency across different GPU preset levels. Use IPVTL's internal logging to capture performance metrics and GPU-Z for detailed hardware telemetry.
