IPTV OTT Encoding & Streaming
Secure Reliable Transport (SRT) Protocol
What is Secure Reliable Transport (SRT)?
 Secure Reliable Transport (SRT) is an open source video transport protocol developed
originally by Haivision. It works on UDP but provides reliable transmission similar to TCP,
by utilizing similar methods for connection, sequence numbers, acknowledgements and
re-transmission of lost packets.
Secure Reliable Transport (SRT) is an open source video transport protocol developed
originally by Haivision. It works on UDP but provides reliable transmission similar to TCP,
by utilizing similar methods for connection, sequence numbers, acknowledgements and
re-transmission of lost packets.
SRT makes it possible to send MPEG transport streams over the public internet with low latency and high reliability, perfect for professional IPTV streaming applications.
SRT Streaming Configuration
Stream from SRT Source (Caller Mode vs Listener Mode)
To stream from an SRT source, select srt as the source type and enter the SRT URL in
the source address, for example: srt://192.168.1.2:1234
Source Mode Options: SRT source operates in caller mode by default, which means it
initiates a
connection to the source server to start streaming. If you want to use listener mode
instead, change the address to a local host address, for example
srt://0.0.0.0:1234, and set the SRT mode in the advanced config below. In
listener mode, it waits for the remote peer to connect before streaming begins.
Stream P2P SRT Output (P2P Streaming Mode)
Select SRT in the Target Format and enter the destination IP address where you want
to deliver the stream. For example: srt://0.0.0.0:1234
Output Mode Options: SRT output operates in listener mode by default, which means it
waits for a
remote peer to connect before streaming starts. If you want to use caller mode instead,
change the address to a remote host address, for example
srt://192.168.1.2:1234, and set the SRT mode in the advanced config below. In
caller mode, it initiates a connection to the remote peer and starts streaming.
Network Redundancy & Path Bonding
SRT Path Redundancy & Connection Bonding
IPVTL supports SRT connection bonding for network failover. By using two or more network interfaces, you can stream with network path redundancy like Haivision SRT Gateway. This ensures reliable streaming even if one connection fails. See the details below.
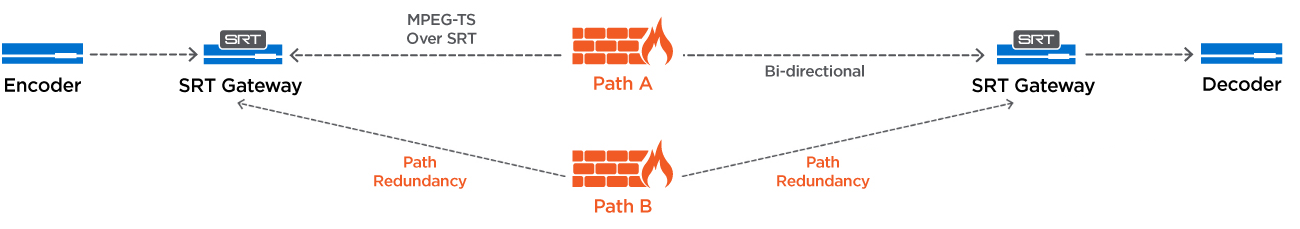
Setting Up Connection Bonding
To enable Connection Bonding, you need at least two internet connections (at least two network interfaces configured on your computer). Open Advanced Format Settings and go to the SRT Config tab to set up SRT connection bonding.
Listener Mode Configuration
For SRT listener mode, Connection Bonding is enabled by default and no additional configuration is needed.
Caller Mode Configuration & Bonding Types
For SRT caller mode, you can set a second remote IP address in Connection #2 as a backup connection route to the peer SRT server in Connection #1. For each connection, you can optionally specify a local network interface. You can set up bonded connections either with two different remote addresses, or with a same remote address from two different local addresses. Either method establishes two separate streaming paths.
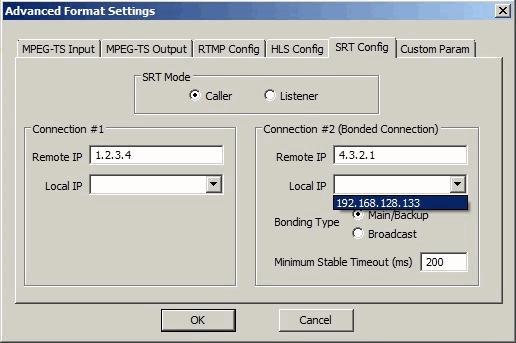
Bonding Modes & Port Configuration
Note that bonded connections share the same port number, so it is omitted in the address field here. Bonding type defaults to Main/Backup (Active-Standby), which means only one link is used for streaming at any given time. For advanced users, Broadcast (Active-Active) is also supported, in which case both links stream simultaneously, doubling network traffic.
Tuning Connection Stability
There is another option called Minimum Stable Timeout that determines when an SRT connection is considered unstable and should be switched to another. Do not modify it unless you fully understand what it does.
Advanced Network Configuration
Network Routing & Redundancy Setup
IMPORTANT: On a PC with two network interfaces enabled, one is typically selected as the default gateway in the routing table, as shown below:
# route -n
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
0.0.0.0 1.2.3.4 0.0.0.0 UG 200 0 0 eth1
0.0.0.0 4.3.2.1 0.0.0.0 UG 300 0 0 eth2
In this example, both the SRT main and backup streams go through eth1
(determined by Metric), which prevents connection bonding from working. To make SRT backup
connection work properly, you must set up load balancing to route it through
eth2 instead. This can be done by adding a custom network route.
Linux Network Route Configuration
To add a custom route in Linux (where x.x.x.x is the peer address of the SRT
backup endpoint and eth2 is the local backup network interface):
# route add -host x.x.x.x gw 4.3.2.1 dev eth2
Make sure the route added successfully in system route table:
# route -n
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
x.x.x.x 4.3.2.1 255.255.255.255 UGH 0 0 0 eth2
Note that the route added above is temporary and does not persist after a system reboot.
Create a network startup script (such as netplan) to make it permanent and run
automatically.
Windows Network Route Configuration
To add a custom route in Windows (where x.x.x.x is the peer address of the SRT backup endpoint and 2 is the local backup network interface ID):
# route -p add x.x.x.x mask 255.255.255.255 4.3.2.1 if 2
Note that the option "-p" ensures the route persists even after a system
reboot.
Enhanced Streaming Performance with SRT
Hardware Acceleration Options
For superior encoding performance with SRT streaming, consider accelerating your streaming pipeline with:
- NVIDIA GPU acceleration for H.264/H.265 encoding optimization
- Intel GPU integration for efficient real-time transcoding
- NETINT VPU hardware for ultra-low latency streaming
Complementary Streaming Features
Enhance your SRT streaming setup with additional professional features:
- Professional video codecs selection and optimization
- Adaptive multi-bitrate streaming for optimal quality
- Seamless streaming transitions for broadcast reliability
- Video overlay and graphics for professional branding
- HLS streaming protocol for wide device compatibility
- RTMP live streaming for CDN distribution
